

In deuterostomes, the zygote undergoes radial cleavage, a process in which the cells divide at right angles to one another. The removal of any cell from the developing embryo will result in abnormal development, and individually removed cells will not develop into complete larvae. Spiral cleavage is also called determinate cleavage, because the function of the cells is determined early in the cleavage process. Another superphyletic term used to describe animals with spiral cleavage is Spiralia. The realignment of the mitotic spindle causes each cell to divide unequally, resulting in a spiral displacement of small cells, the micromeres, that come to sit atop the border between larger cells, the macromeres. In protostomes, the developing zygote undergoes spiral cleavage, a process in which the cells divide at a 45° angle to one another due to a realignment of the mitotic spindle.
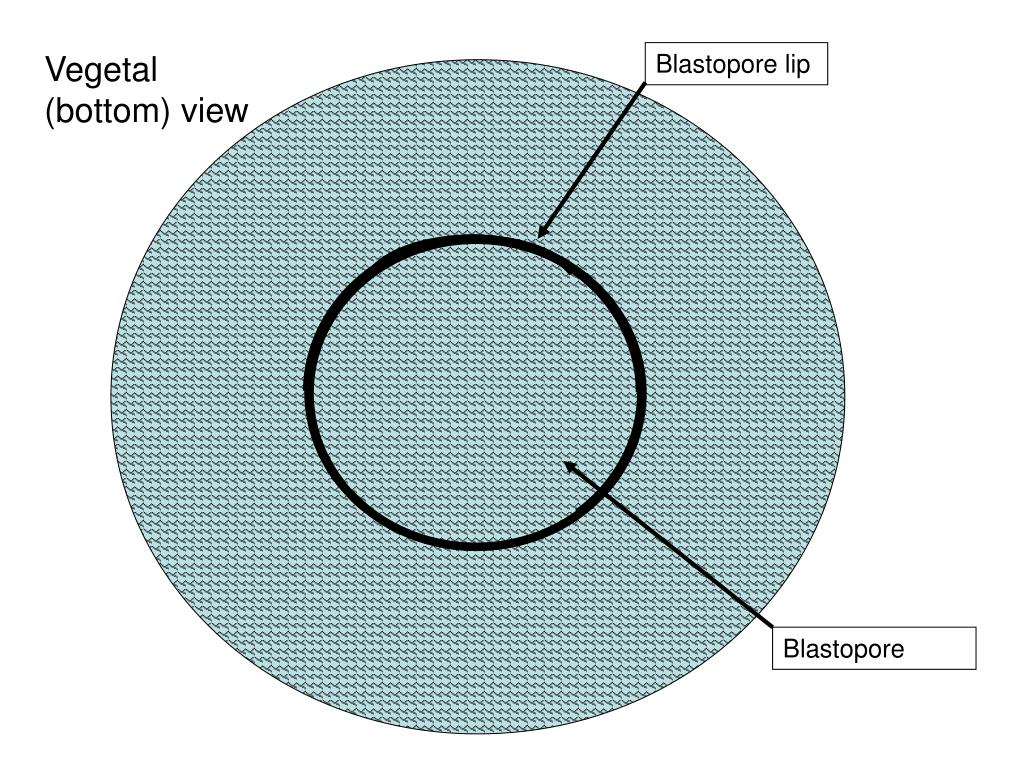
Origin of mesoderm: pouches off gut (endoderm)Ĭleavage pattern refers to the process of cell division from one fertilized cell, the zygote, into hundreds of cells, the embryo.Origin of mesoderm arises from mesentoblast (4d cells).These developmental features are different in the two groups and can be summarized as follows: Origin of mesoderm (the "middle" embryonic tissue layer between ectoderm and endoderm that forms various structures such as muscles and skeleton).Embryonic cleavage pattern (that is, how the zygote divides to become a multicellular animal).Historically, the two groups are distinguished by the following criteria: Grobben was not the first biologist to recognize the distinction between these two groups, but he was the first to place importance on the fate of the blastopore as a major distinguishing criterion. Traditionally, the protostomes include the Annelida, Arthropoda, and Mollusca, and the deuterostomes comprise the Echinodermata and Chordata. Protostomia and Deuterostomia are considered super-phyletic taxa, each containing a variety of animal phyla. Animals in which the blastopore becomes the mouth are called protostomes those in which the mouth develops after the anus are called deuterostomes (from the Greek "deutero," meaning second, and "stoma," meaning mouth). It distinguishes a group of invertebrate animals based upon the fate of the blastopore (the first opening of the early digestive tract) during embryonic development. The term Protostomia (from the Greek "proto," meaning first, and "stoma," meaning mouth) was coined by the biologist Karl Grobben in 1908. The mesoderm is the third germ layer it forms between the endoderm and ectoderm in triploblasts.What is a protostome? Origin of Protostomia The ectoderm develops into the outer epithelial covering of the body surface, the central nervous system, and a few other structures. The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract (including the stomach, intestines, liver, and pancreas), as well as to the lining of the trachea, bronchi, and lungs of the respiratory tract, along with a few other structures. Statement d is false.Įach of the three germ layers is programmed to give rise to particular body tissues and organs. The mesoderm gives rise to the central nervous system.The endoderm gives rise to the lining of the digestive tract and the respiratory tract.Animals that display bilateral symmetry are triploblasts.Animals that display radial symmetry are diploblasts.Which of the following statements about diploblasts and triploblasts is false?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
